Consulting Services
Land Conservation
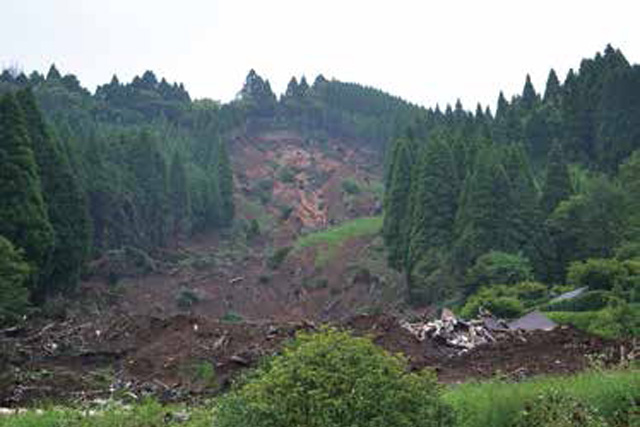

Slope Disaster Management
Japan is located in the Pacific Ring of Fire volcanic zone and has been hit by numerous sediment-related disasters caused by volcanic eruptions and large earthquakes. In addition, in recent years disasters caused by torrential rains brought on by climate change have been increasing as well. In order to protect human life and infrastructure from sediment-related disasters such as slope failure, debris flow, and landslides, it is important to predict their occurrence and take necessary countermeasures.
Based on the extensive experience we have accumulated through our consulting services, we provide appropriate investigation and design for countermeasures against sediment-related disasters occurring on natural and artificial slopes.
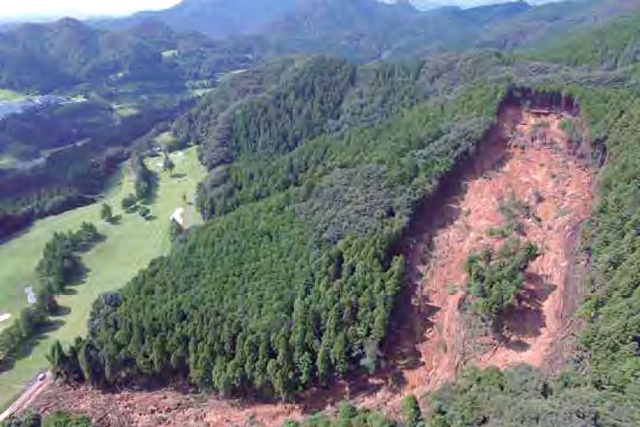

Forest Conservation and Afforestation
In Japan, forests account for about 70% of the country’s land and serve many vital functions such as biodiversity preservation, sediment-related disaster prevention, water source protection, and rest and recreation. In order to preserve the multifaceted function of these forests, it is necessary to protect mountain slopes from erosion and restore forests damaged by development and other causes.
We have been engaged in investigation and design for countermeasures to protect mountain slopes from landslides, slope failure, debris flow, etc.
Furthermore, it is necessary to properly implement forest management such as planting, cultivation, logging, pest and insect damage control, and forest fire prevention in order to maintain and restore forests. Forest roads are indispensable for these activities. We have formulated and proposed a comprehensive plan concerning the investigation and design of forest roads and road structures as well as maintenance plans.
The Great East Japan Earthquake caused tremendous damage to the coastal disaster prevention forest. In rebuilding such tsunami-affected areas, we have formulated a grand design for restoration of coastal disaster prevention forests that takes into consideration their damage reduction effect against tsunami in addition to disaster prevention functions such as sand and wind damage fortification.
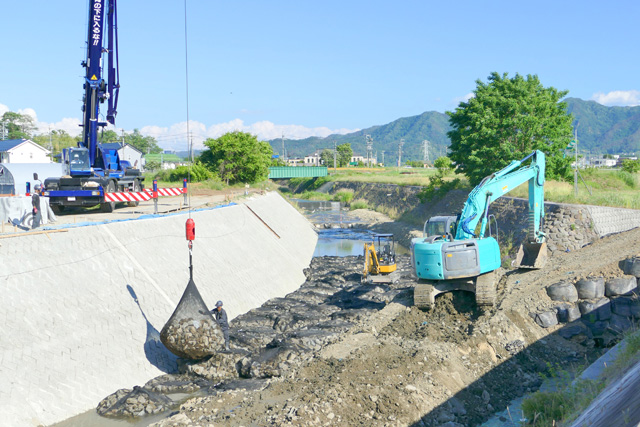

River and Coastal Conservation and Sediment-Related Disaster Preventiont
In order to conserve river environments, it is necessary to comprehensively manage them by preventing the occurrence of floods and maintaining the normal function of running water.
Erosion control is aimed at ensuring regional safety from sediment-related disasters such as debris flow, landslides and slope failure, restoring devastated mountainous areas with vegetation, and creating a safe and livable area.
As coasts are exposed to many dangers such as tsunami caused by large earthquakes and storm surge and waves due to typhoons, it is important to devise the proper use of the coast through maintaining and preserving the coastal environment as well as protecting it from damage due to sea level fluctuation and ground subsidence.
We provide comprehensive technical services from planning to investigation and design for preserving rivers and coasts and preventing sediment-related disasters.
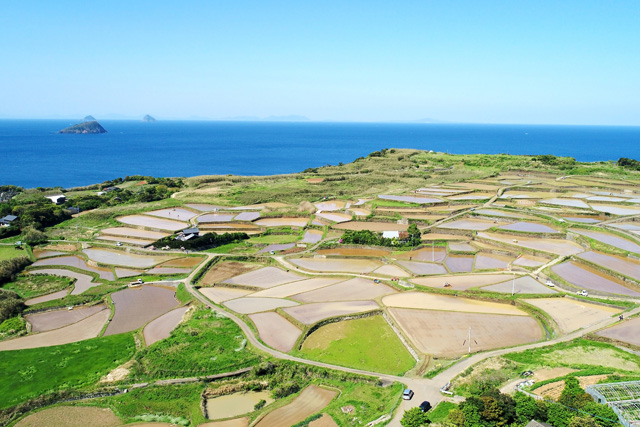

Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction
Due to geographical, topographical and meteoro-logical conditions, Japan is subject to frequent natural disasters such as typhoons, torrential rains and heavy snowfalls, as well as earthquakes and tsunami. In large-scale disasters, no one is more familiar with the actual conditions of the community than local residents, and their disaster risk reduction activities are essential. In recent years, the important role played by the local community in times of disaster, also referred to as mutual help or mutual assistance, has been widely recognized, and disaster risk reduction activities at the regional level are being promoted.
At the same time, however, local communities face many problems due to changes in the population structure, decline of the regional economy, and dilution of local connections. It is therefore necessary to identify these issues and consider what a local community should be as well as the ideal features of community-based disaster risk reduction activities.
We prepare various methods for local communities to practice disaster risk reduction activities such as hazard maps, communication methods, and evacuation methods, as well as provide support suited to each community.
Global Environmental Conservation

Environmental Conservation
Based on the concept of “earth, water and vegetation”, we engage in environmental conservation with “global environmental conservation” as our ultimate goal. For each of the various themes this encompasses, such as maintaining biodiversity, measures against soil contamination, preventing water pollution, and recovery of devastated vegetation, we have taken on the challenge of finding solutions that promote harmony between an ideal natural environment and social demands.
Especially with regard to groundwater and soil, we propose optimal countermeasures through elucidation of the mechanisms for such as things as depletion of groundwater resources by excessive pumping and contamination of groundwater and soil by naturally occurring heavy metals and illegally dumped waste, thereby contributing to a reduction in risks to the natural and social environment.

Geospherical Environment
Japan is constantly exposed to the risk of natural disasters such as landslides, floods, tsunami, and earthquakes caused by typhoons, torrential rain, large earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other phenomena. Therefore, accurate information concerning the ground is indispensable in order to respond to such natural disasters and build a society resilient to disasters.
To prepare prevention plans and design countermeasure structures for various disasters, we conduct investigations to obtain detailed information about the ground such as topography, geology, and groundwater. Based on the results, the most effective plans and designs for disaster prevention and reduction measures are formulated.
Construction and Supervision
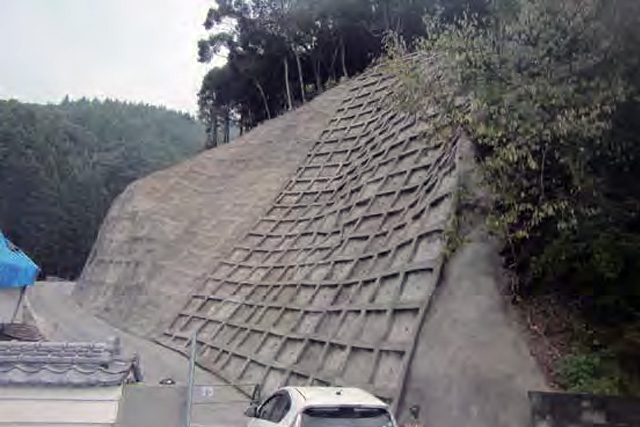

Construction of Landslide Prevention Measures
Landslide prevention measures are broadly classified into two types of works: control works and restraint works. Control works are intended to remove or mitigate natural factors such as topography, geology, and groundwater that could lead to the occurrence of a landslide. On the other hand, restraint works aim to stabilize a slope through the construction of structural elements.
We have an extensive track record with anchor works, which are representative of restraint works, and are also developing new anchoring technologies such as SSL anchor works.Drainage well works are the most common kind of control works, and we have experience in the construction of about 800 of these. Moreover, we are developing construction techniques to match various natural conditions.

Construction of Slope Disaster Prevention
In Japan, with its steep terrain, complex geological features, and vulnerability to
typhoons and earthquakes, slope disaster prevention technology to prevent phenomena
that occur on natural slopes, cut earth, and embankments such as rock fall and slope collapse is extremely important.
Applying the extensive knowledge and techniques we have accumulated through our consulting work in slope disaster prevention works to construction and supervision, we carry out safe and sustainable countermeasure works for disaster recovery and slope disaster prevention.
In order to contribute to global environmental conservation by reducing CO2 emissions, we are also taking on the challenge of revegetation in sterile soil conditions such as highly acidic soils, highly basic soils, steep bedrock and extremely arid land under the theme of “restoration to a natural state”.
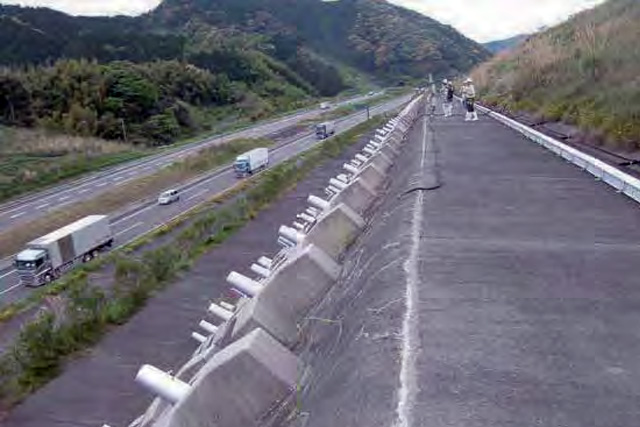

Countermeasures Against Aging
Based on our experience with frequent large-scale disasters, we have promoted infrastructure development in Japan necessary for adapting to severe topographical and weather conditions. In the process, advancements have been made in the safety and convenience of infrastructure functions and in construction technology with the development and introduction of new technologies. However, a portion of existing infrastructures have aged, and in order to secure the safety and security of citizens in response to various large-scale disasters expected to occur in the future, it is necessary to strengthen the functions of infrastructures instead of simply extending their lifecycles.
We possess superior technologies for inspection, investigation and diagnosis of infrastructures, particularly road structures, erosion control structures, river structures and landslide prevention installations, and propose a system enabling consistency from accurate diagnosis to selection of optimal maintenance methods which will also reduce lifecycle costs.
Research and Development
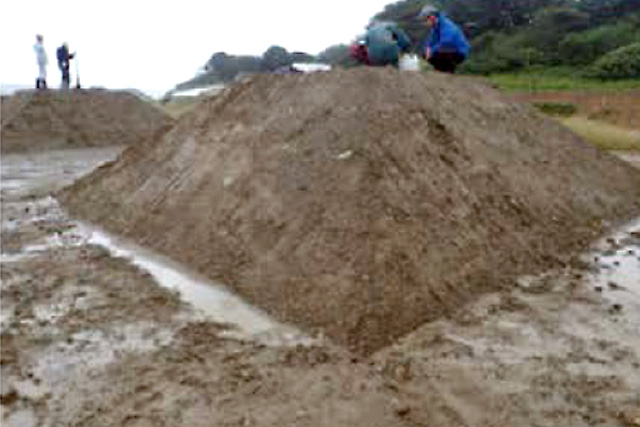

Development of Afforestation Technology
In order to revegetate areas such as devastated forests, comprehensive consideration of local conditions such as weather conditions, soil, and geology must be taken. It is also important to select plant species suitable for regional characteristics and to secure planting material.
We have developed a variety of afforestation technologies such as the “Tough Green Method” and the plant growth promoter “Fujimin”. Made from fulvic acid, Fujimin has the effect of promoting stabilization of pH conditions and aggregation of soil as well as helping mineral absorption. Fujimin has been registered on the Organic JAS Material List.
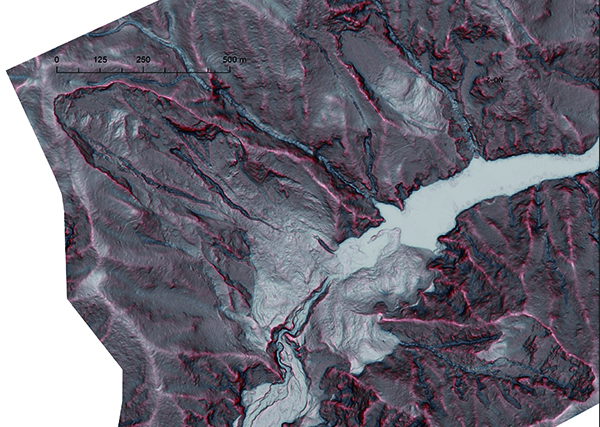
Development of Geospatial Information Technology
In recent years, achievements have been made to improve productivity and ensure quality in the overall construction production process through the use of computerized construction, or “i-Construction”. This method utilizes information and communications technology (ICT) to realize highly efficient and accurate construction by exchanging electronic infor-mation obtained from each individual process.
Three-dimensional surveying by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) that are capable of high-precision and speedy surveying of broad areas of construction sites is considered extremely effective for i-Construction. We deploy UAV nationwide to take aerial photographs in times of disaster, quickly creating orthoimages and various representation diagrams for assessing disaster conditions and considering countermeasures.
In addition, we are promoting the development of geospatial information technology in a wide range of fields such as infrastructure maintenance and forest conservation.
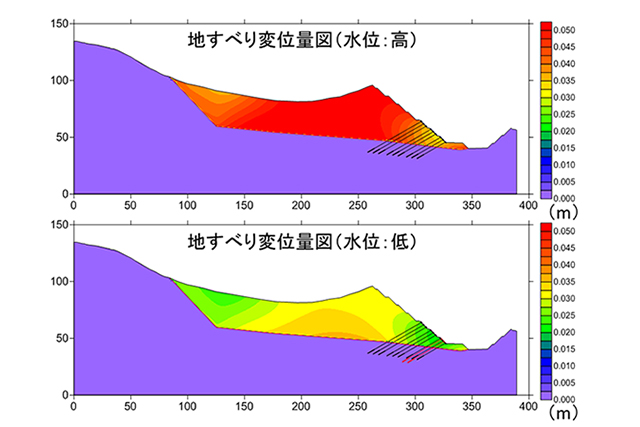
Development of 3D Simulation Technology
In recent years, countermeasures against disasters have shifted to policies that emphasize “mitigation of disaster” to minimize damage. In order to realize these policies, a disaster management plan that supports evacuation and relief in the event of a disaster is necessary. Simulation technology for predicting phenomena and damage of disasters is extremely effective in formulating disaster prevention plans.
3D simulation technology is already used in the design of disaster prevention facilities, and we are also developing 3D simulation techniques to create flood risk maps, earthquake damage maps and hazard maps for sediment-related disasters, etc.
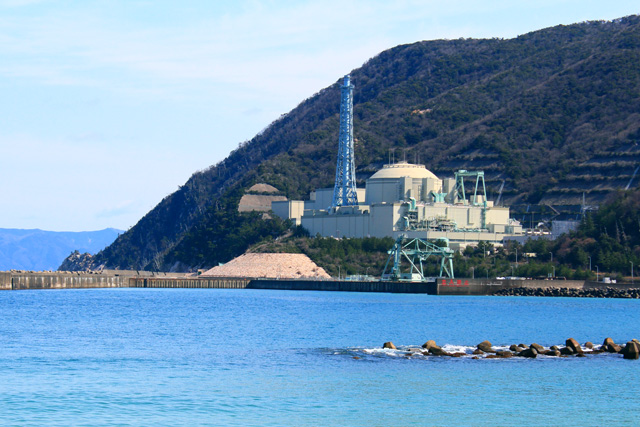

Improvement of Radioactivity Concentration Measurement Methods
A large amount of radioactive substances were released due to the nuclear accident after the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and tsunami. Consequently, the Japanese government enacted special measures, the purpose of which was to promptly reduce the impact of environmental pollution on human health and living environment. To achieve this, monitoring and measurement of environmental pollution has been implemented by the national government, local governments, and relevant nuclear power plant operators.
We have been working on environmental radiation monitoring in forests where similar studies have not been conducted since the nuclear accident occurred. We continue to conduct research and development so that our survey methods will be suitable for future nationwide standards.
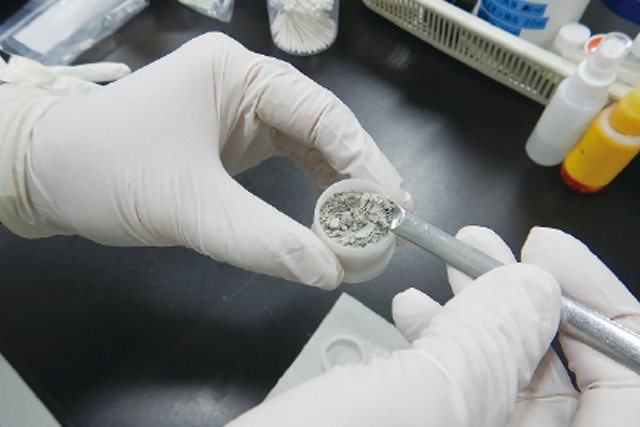

Laboratory Testing of Soil and Rocks
Our laboratory for testing of soil and rocks contains various testing equipment conforming to Japan Industrial Standards (JIS) and Japanese Geotechnical Society Standards (JGS), and tests are conducted on various physical properties of soil and rocks.
In the case of sediment-related disasters in particular, accurately assessing the physical properties of the soil and rocks composing the slope and the landslide slip surface are extremely important for analyzing the stability of the ground. Therefore, we are conducting research and development on testing equipment, testing methods and analysis of test results, with an eye on 3D simulation applications as well.
project
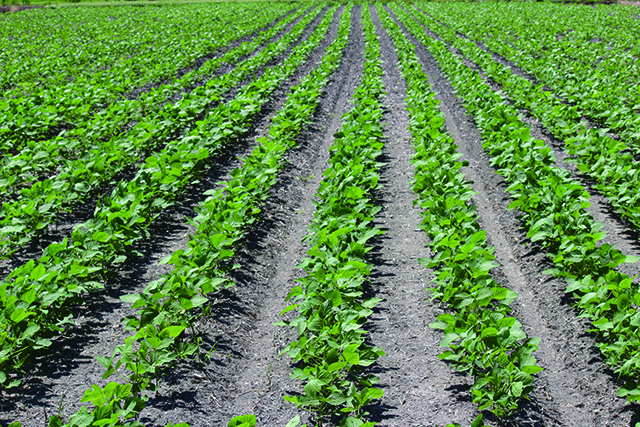

Paraguay project
Our project proposal for applying agricultural land environment improvement using Fujimin for Paraguay has been adopted by Japan International Cooperation Agency(JICA) for the framework of the SDGs Business Verification Survey with the Private Sector. We will challenge to improve the farmland where crop production is difficult, increase the yield of farm products, and correct poverty disparities by means of making farmers’ income increase.
With Fujimin(concentrated fulvic acid), we further plan to expand our efforts on the soil im-provement of the farmland where soil depletion occurs due to monocropping or salt accumulation that accounts for one-fifth of the world irrigated land.



